Nitrite
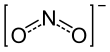
Nitrite (a-siau sng iâm; hàn-gú: 亞硝酸鹽) im lī-tsú ê huà-ha̍k sik uî NO−2. Nitrite (a-siau sng iâm, tsú-iàu sī a-siau sng iâm natrium (sodium nitrite)) kóng-huàn iōng-teh kui-ê huà-ha̍k hām tsè-io̍h.[1] Nitrite im lī-tsú sī tsū-liân-kài tām-sòo sûn-khuân tang-tiong phóo-phiàn tsûn-tsāi ê tiong-kan thé. Nitrite tsit-ê bîng-tshing mā tsí-tshut kū-iú -ONO ki-thuân ê iú-ki hua-ha̍p-bu̍t, in sī "a-siau sng" (Nitrous acid) ê ester.
| |||
| Hō-miâ | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC hō-miâ
Nitrite
| |||
| Hē-thóng-tek IUPAC hō-miâ
dioxidonitrate(1−) | |||
| Kî-tha hō-miâ
nitrite
| |||
| Sek-pia̍t-hō | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number | 233-272-6 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Sèng-chit | |||
| NO− 2 | |||
| Mole chit-liōng | 46.01 g·mol−1 | ||
| Conjugate acid | Nitrous acid | ||
Tû-liáu te̍k-pia̍t chí chhut, chu-liāu sī kun-kù bu̍t-chit ê piau-chún chōng-thài (tī 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox chham-chiàu | |||
Tsù-kái
siu-kái- ↑ Laue, Wolfgang; Thiemann, Michael; Scheibler, Erich; Wiegand, Karl Wilhelm (2006). "Nitrates and Nitrites". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_265.
Tsham-khó bûn-hiàn
siu-kái- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd pán.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Coudray, Guillaume, Who poisoned your bacon. London: Icon Books, 2021. ISBN 9-781-78578612-9
Tsham-ua̍t
siu-kái- Curing (food preservation)
- Alkyl nitrites