Liû-hoà chúi-sò͘
Liû-hoà chúi-sò͘ (硫化水素, Eng-gí: hydrogen sulfide), hoà-ha̍k-sek H2S, sī chi̍t-ê liû-hông (S) goân-chú kap nn̄g-ê chúi-sò͘ (H) ê cho͘-ha̍p.
| |||
| |||
| Hō-miâ | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hē-thóng-tek IUPAC hō-miâ
Hydrogen sulfide[1] | |||
Kî-tha hō-miâ
| |||
| Sek-pia̍t-hō | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | B01206 | ||
| 3535004 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.070 | ||
| EC Number | 231-977-3 | ||
| 303 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Hydrogen+sulfide | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number | MX1225000 | ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1053 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Sèng-chit | |||
| H2S | |||
| Mole chit-liōng | 34.08 g·mol−1 | ||
| Gōa-māu | Colorless gas | ||
| Khì-bī | Pungent, like that of rotten eggs | ||
| Bi̍t-tō͘ | 1.363 g dm−3 | ||
| Iûⁿ-tiám | −82 °C (−116 °F; 191 K) | ||
| Hut-tiám | −60 °C (−76 °F; 213 K) | ||
| 4 g dm−3 (at 20 °C) | |||
| Cheng-khì-ap | 1740 kPa (at 21 °C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.0[2][3] | ||
| Conjugate acid | Sulfonium | ||
| Conjugate base | Bisulfide | ||
Chû-hòa-lu̍t (χ)
|
−25.5·10−6 cm3/mol | ||
Khut-chiat-lu̍t (nD)
|
1.000644 (0 °C)[4] | ||
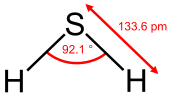
| Kò͘-chō | |||
| C2v | |||
| Bent | |||
| 0.97 D | |||
| Jia̍t-hòa-ha̍k | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
1.003 J K−1 g−1 | ||
Piau-chún mole
entropy (S |
206 J mol−1 K−1[5] | ||
Piau-chún hêng-sêng
enthalpy (ΔfH |
−21 kJ mol−1[5] | ||
| Gûi-hiám | |||
| Main hazards | Flammable and highly toxic | ||
| GHS pictograms | Pang-bô͘:GHS02Pang-bô͘:GHS06Pang-bô͘:GHS09 | ||
| GHS signal word | Danger | ||
| 指令碼錯誤:沒有「GHS phrases」這個模組。 | |||
| 指令碼錯誤:沒有「GHS phrases」這個模組。 | |||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Ín-hóe-tiám | −82.4 °C (−116.3 °F; 190.8 K)[8] | ||
| 232 °C (450 °F; 505 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 4.3–46% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
| ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
| ||
| Bí-kok kiān-hong pī-pha̍k chè-hān (NIOSH): | |||
PEL (Ē-thong-kòe)
|
C 20 ppm; 50 ppm [10-minute maximum peak][6] | ||
REL (Chhui-chiàn)
|
C 10 ppm (15 mg/m3) [10-minute][6] | ||
IDLH (Chek-sî gûi-hiám)
|
100 ppm[6] | ||
| Koan-liân hòa-ha̍p-bu̍t | |||
Related hydrogen chalcogenides
|
|||
Koan-liân hòa-ha̍p-bu̍t
|
Phosphine | ||
Tû-liáu te̍k-pia̍t chí chhut, chu-liāu sī kun-kù bu̍t-chit ê piau-chún chōng-thài (tī 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox chham-chiàu | |||
Chù-kái
siu-kái- ↑ "Hydrogen Sulfide - PubChem Public Chemical Database". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- ↑ Perrin, D.D. (1982). Ionisation Constants of Inorganic Acids and Bases in Aqueous Solution (2nd pán.). Oxford: Pergamon Press.
- ↑ Bruckenstein, S.; Kolthoff, I.M., in Kolthoff, I.M.; Elving, P.J. Treatise on Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 1, pt. 1; Wiley, NY, 1959, pp. 432–433.
- ↑ Patnaik, Pradyot (2002). Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-049439-8.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles (6th pán.). Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A23. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0337". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Hydrogen sulfide". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "Hydrogen sulfide". npi.gov.au.
| Pún bûn-chiuⁿ sī chi̍t phiⁿ phí-á-kiáⁿ. Lí thang tàu khok-chhiong lâi pang-chō͘ Wikipedia. |