Turkmen-gí
Turkmen-gí sī Turkmenistan ê koan-hong gí-giân.
| Turkmen | |
|---|---|
|
türkmençe, türkmen dili, түркменче, түркмен дили, تۆرکمن ديلی ,تۆرکمنچه | |
 Turkmen in the Latin, Cyrillic, and Perso-Arabic Alphabets | |
| Goân-chū kok-ka | Turkmenistan, Russia, Iran, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan[1][2] |
| Bîn-cho̍k | Turkmens |
| bú-gí sú-iōng-chiá | 11 million[3] (2009–2015)[4] |
| Gí-hē |
Turkic
|
| Hong-giân | |
| Bûn-jī hē-thóng |
Latin (Official, Turkmen alphabet), Perso-Arabic, Cyrillic Turkmen Braille |
| Koaⁿ-hong tē-ūi | |
| Koaⁿ-hong gí-giân | Pang-bô͘:TKM |
| Gí-giân tāi-bé | |
| ISO 639-1 |
tk |
| ISO 639-2 |
tuk |
| ISO 639-3 |
tuk |
| Glottolog |
turk1304 |
| Linguasphere |
Part of 44-AAB-a |
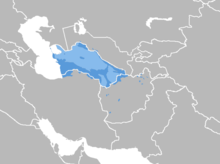 The distribution of the Turkmen language in Central Asia | |
Tsù-kái
siu-kái- ↑ Ethnic composition, language and citizenship of the population of the Republic of Tajikistan, Volume III (in Russian)
- ↑ Ethnic Turkmen of Tajikistan Preserve Traditions of Their Ancestors
- ↑ Ahmet Cuneyd Tantug. A MT System from Turkmen to Turkish Employing Finite State and Statistical Methods. Istanbul Technical University. 2008. p.2
- ↑ Turkmen at Ethnologue (21st ed., 2018)
| Pún bûn-chiuⁿ sī chi̍t phiⁿ phí-á-kiáⁿ. Lí thang tàu khok-chhiong lâi pang-chō͘ Wikipedia. |