Kám-mō͘
Kám-mō͘ (感冒), mā thang kiò chò hong-siâ (風邪), siong-hong (傷風), sī téng ho͘-khip hē-thóng (phīⁿ-á kap nâ-aû) khì hō͘ pēⁿ-to̍k oè--tio̍h ê 1 chióng thoân-jiám-pēⁿ. Chèng-thaû phēng liû-hêng-sèng kám-mō͘ khah un-hô, pau-koah ē phah-kha-chhiùⁿ, chhǹg-phīⁿ, sat-phiⁿ (nasal congestion); nâ-aû ngiau-ngiau (scratchy), sng-thiàⁿ (sore), ū thâm; ka-saù, thaû-thiàⁿ, lâng siān-siān téng-téng. Tiāⁿ ē koâⁿ beh 3-5 kang, soà--lo̍h siōng kú koh saù beh 3 lé-pài. Kám-mō͘ sī lâng siōng chia̍p hoat-seng ê pēⁿ, 1 ê lâng 1 nî pêng-kin ē tio̍h 1 pái khah ke; ū ê só͘-chāi koh ē chhiau-koè 3 pái. Gín-á, kò͘ gín-á--ê, ha̍k-haū, chhù--nih siōng-kài ē tì tio̍h kám-mō͘.
| Common cold | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Cold, acute viral nasopharyngitis, nasopharyngitis, viral rhinitis, rhinopharyngitis, acute coryza, head cold,[1] upper respiratory tract infection (URTI)[2] |
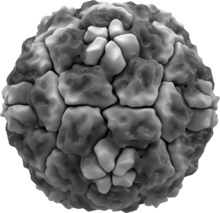 | |
| A representation of the molecular surface of one variant of human rhinovirus | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Cough, sore throat, runny nose, fever[3][4] |
| Complications | Usually none, but occasionally otitis media, sinusitis, pneumonia and sepsis can occur[5] |
| Usual onset | ~2 days from exposure[6] |
| Duration | 1–3 weeks[3][7] |
| Causes | Viral (usually Rhinovirus)[8] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms |
| Differential diagnosis | Allergic rhinitis, bronchitis, bronchiolitis,[9] pertussis, sinusitis[5] |
| Prevention | Hand washing, face masks, cough etiquette, avoiding sick people[3][10] |
| Treatment | Symptomatic therapy,[3] zinc[11] |
| Medication | NSAIDs[12] |
| Frequency | 2–3 per year (adults); 6–8 per year (children)[13] |
Kám-mō͘ kap liû-kám bô kâng. Tio̍h liû-kám ē hoat-sio kah chin lī-hāi, ùi-koâⁿ, sin-thé kap kin-bah sng-thiàⁿ (muscle aches). Kám-mō͘ khah bē sí-lâng, m̄-koh nā choán chò hì-iām tō chin gûi-hiám.
Kám-mō͘ ê pēⁿ-to̍k piàn-hoà thài kín, kaù taⁿ e̍k-biâu iáu chò bô lō͘ lâi.
Tsù-kái
siu-kái- ↑ Pramod JR (2008). Textbook of Oral Medicine. Jaypee Brothers Publishers. p. 336. ISBN 978-81-8061-562-7. goân-loē-iông tī 29 May 2016 hőng khó͘-pih. Unknown parameter
|url-status=ignored (help) - ↑ Lee H, Kang B, Hong M, Lee HL, Choi JY, Lee JA (July 2020). "Eunkyosan for the common cold: A PRISMA-compliment systematic review of randomised, controlled trials". Medicine. 99 (31): e21415. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000021415. PMC 7402720 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32756141 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Ín-iōng chhò-gō͘: Bû-hāu ê
<ref>tag; chhōe bô chí-miâ ê ref bûn-jīCDC2015 - ↑ Ín-iōng chhò-gō͘: Bû-hāu ê
<ref>tag; chhōe bô chí-miâ ê ref bûn-jīEccles2005 - ↑ 5.0 5.1 Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ (2014). Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases (ēng Eng-gí). Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 750. ISBN 978-1-4557-4801-3. goân-loē-iông tī 8 September 2017 hőng khó͘-pih. Unknown parameter
|url-status=ignored (help) - ↑ Ín-iōng chhò-gō͘: Bû-hāu ê
<ref>tag; chhōe bô chí-miâ ê ref bûn-jīCMAJ2014 - ↑ Ín-iōng chhò-gō͘: Bû-hāu ê
<ref>tag; chhōe bô chí-miâ ê ref bûn-jīHeik2003 - ↑ Ín-iōng chhò-gō͘: Bû-hāu ê
<ref>tag; chhōe bô chí-miâ ê ref bûn-jīCE11 - ↑ "Bronchiolitis: Symptoms and Causes". Mayo Clinic. 3 May 2022 khòaⁿ--ê.
- ↑ Ín-iōng chhò-gō͘: Bû-hāu ê
<ref>tag; chhōe bô chí-miâ ê ref bûn-jīE209 - ↑ Ín-iōng chhò-gō͘: Bû-hāu ê
<ref>tag; chhōe bô chí-miâ ê ref bûn-jīNIH2016Zinc - ↑ Ín-iōng chhò-gō͘: Bû-hāu ê
<ref>tag; chhōe bô chí-miâ ê ref bûn-jīKim2015 - ↑ Ín-iōng chhò-gō͘: Bû-hāu ê
<ref>tag; chhōe bô chí-miâ ê ref bûn-jīAFP07
Tsham-khó bûn-hèn
siu-kái- Eccles R, Weber O, pian. (2009). Common Cold (Illustrated pán.). Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3-7643-9912-2.
Guā-pōo lên-ket
siu-kái| Pún bûn-chiuⁿ sī chi̍t phiⁿ phí-á-kiáⁿ. Lí thang tàu khok-chhiong lâi pang-chō͘ Wikipedia. |