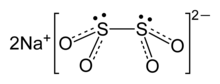
Sodium dithionite
Sodium dithionite (mā kiò-tsò sodium hydrosulfite; hàn-gú: 連二亞硫酸鈉 (lên-jī a-liû-sng la̽p), 低亞硫酸鈉 (kē a-liû-sng la̽p), 二硫亞磺酸鈉 (jī-liû a-hông-sng la̽p)) sī pe̍h-sik ket-tsiñ-sìng ê hún-bua̍h, ū liû-hông khì-bī. Sui-jên teh ta-sò ê khong-khì tang-tiong sī ún-tīng ê, m̄-koh sio-tsuí hām sng iông-ı̽k lāi-té ê hun-kái. sio̍k-tshing pó-hiám-hún,hun-tsí-sik Na2S2O4, sī tsi̍t-tsióng kiông huân-guân-tse, ē-tàng tsè-sîng si̍t-phín phiò-pe̽h-che.[1]
| |

| |

| |
| Hō-miâ | |
|---|---|
| Kî-tha hō-miâ
D-Ox, Hydrolin, Reductone
sodium hydrosulfite, sodium sulfoxylate, Sulfoxylate Vatrolite, Virtex L Hydrosulfit, Prayon Blankit, Albite A, Konite Zepar, Burmol, Arostit | |
| Sek-pia̍t-hō | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.991 |
| EC Number | 231-890-0 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | JP2100000 |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1384 |
| |
| |
| Sèng-chit | |
| Na2S2O4 | |
| Mole chit-liōng | 174.107 g/mol (anhydrous) 210.146 g/mol (dihydrate) |
| Gōa-māu | white to grayish crystalline powder light-lemon colored flakes |
| Khì-bī | faint sulfur odor |
| Bi̍t-tō͘ | 2.38 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 1.58 g/cm3 (dihydrate) |
| Iûⁿ-tiám | 52 °C (126 °F; 325 K) |
| Hut-tiám | Decomposes |
| 18.2 g/100 mL (anhydrous, 20 °C) 21.9 g/100 mL (Dihydrate, 20 °C) | |
| Iûⁿ-kái-tō͘ | slightly soluble in alcohol |
| Gûi-hiám | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS signal word | Danger |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Ín-hóe-tiám | 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) |
| 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) | |
| Koan-liân hòa-ha̍p-bu̍t | |
Kî-tha im-lî-chú
|
Sodium sulfite Sodium sulfate |
Koan-liân hòa-ha̍p-bu̍t
|
Sodium thiosulfate Sodium bisulfite Sodium metabisulfite Sodium bisulfate |
Tû-liáu te̍k-pia̍t chí chhut, chu-liāu sī kun-kù bu̍t-chit ê piau-chún chōng-thài (tī 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox chham-chiàu | |
Tsù-kái
siu-kái- ↑ Weinrach, J. B.; Meyer, D. R.; Guy, J. T.; Michalski, P. E.; Carter, K. L.; Grubisha, D. S.; Bennett, D. W. (1992). "A structural study of sodium dithionite and its ephemeral dihydrate: A new conformation for the dithionite ion". Journal of Crystallographic and Spectroscopic Research. 22 (3): 291–301. doi:10.1007/BF01199531. (Eng-gí)
Tsham-khó bûn-hèn
siu-kái- "Sulfites, Thiosulfates, and Dithionites". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (6th pán.). Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. 2003. pp. 7–11. doi:10.1002/14356007.a25_477. ISBN 978-3-527-30385-4. (Eng-gí)
- Лидин Р.А. и др. Химические свойства неорганических веществ: Учеб. пособие для вузов. — 3-е изд., испр. — М.: Химия, 2000. — 480 с. — ISBN 5-7245-1163-0. (Gô-gú)
Tsham-ua̽t
siu-kái- Kui-keh (ki-su̍t piau-chún) (Kui-keh (ki-su̽t piau-tsún)/Specification (technical standard)/tsu-guân/諸元)
- Chhim-thô lí-hông (Tshim-thô lí-hông/The Scarlet Empress)
- Smolnii ha̍k-īⁿ (Smolnii ha̽k-īñ/Смо́льный институ́т)
- Hiàn-hoat tiōng-tāi sìn-tiâu 19-tiâu (1911) (Hèn-huat tiōng-tāi sìn-tiâu 19-tiâu (1911)/Nineteen Articles)
- Pian-têng kang-kū (Pen-tîng kang-kū/Programming tool)
